Snap-shot assessment of adult mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) densities on the Turks and Caicos Islands, February 2022
Abstract
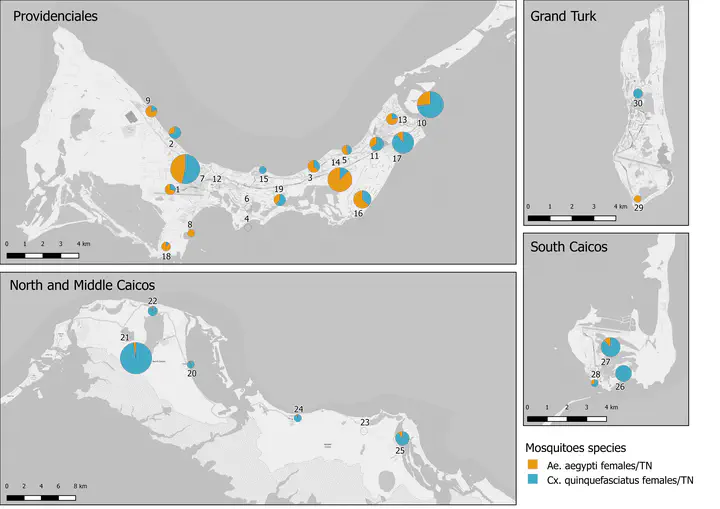
In many of the small island communities of the Caribbean, much of the vector surveillance effort is focused on house-to-house peri-focal surveys to collect data on larval indices. Adult mosquito trapping is not always routine or affordable and is usually focused on ad hoc biting issues or small-scale investigations. This makes understanding the relative importance and densities of the common urban mosquitoes, such as Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus, problematic. This snap-shot survey in February 2022 using BG-Sentinel traps at 30 different locations across five islands of the Turks and Caicos, aimed to provide the first island-wide assessment of urban mosquito densities. In total, 2,820 adult mosquitoes were collected over 285 trap nights. Aedes aegypti was most common on the island of Providenciales, with very low densities recorded on South Caicos, North and Middle Caicos, with Ae. aegypti most highly abundant in the main commercial centres. The highest densities of Cx. quinquefasciatus were trapped on North Caicos. Small numbers of other species were also collected, including the first record of Anopheles in TCI. This established framework of trapping and initial assessment provides a platform for continued monitoring of mosquitoes in TCI to better inform mosquito-borne disease risk assessment and future vector control efforts.